1. Benefits of using for connecting EC2 instances
AWS Systems Manager (SSM) is an AWS service that you can use to view and control your infrastructure on AWS. It can securely connect to a managed node. The SSM Agent is installed in EC2 OS. It is pre-installed on many amazon Machine Images (AMIs).
With SSM:
- No need to open SSH port in security group for EC2
- No need to create and manage SSH keys
And SSM works regardless if the EC2 instance is in public or private (NAT or Endpoint) subnet.
Requirements for SSM working:
- AWS instances:
- SSM agent installed in instance (pre-installed in many AMIs already)
- Connectivity to the AWS public zone endpoint of SSM (IGW, NAT or VPCE)
- IAM role providing permissions
- On-Prem instances:
- SSM agent installed in instance
- Connectivity to the AWS public zone endpoint of SSM (Access to public internet)
- Activation (Activation Code and Actuation ID)
- IAM role providing permissions
2. EC2 Instance in public subnet
- 2.1. Make sure the EC2 instance has a public IP. It could be the public IP assigned during creation, or an Elastic IP.
- 2.2. EC2 instance should have Internet access (for calling SSM endpoint). In public subnet it is done via Internet Gateways. See details from Session Manager prerequisites, in “Connectivity to endpoints” section.
- 2.3. You can use VPC Reachability Analyzer to troubleshoot the connectivity between your EC2 and Internet gateway.
- 2.4. Create an EC2 Instance profile has IAM policy AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore. Read the details from Step 4: Create an IAM instance profile for Systems Manager
- 2.5 Attach the EC2 Instance profile to your instance.
- 2.6 Reboot the EC2 instances.
3. EC2 instance in private subnet, with NAT connectivity
In this case, EC2 instances have no public IP, but they can still talk to internet via NAT.
- 3.1. Make sure EC2 instances in private subnet can access internet, via a NAT Gateway or NAT instance.
- 3.2. The rest will be the same as EC2 instances in public subnet, starting from 2.2
4. EC2 instance in private subnet, without NAT connectivity but VPC endpoints
In this case, the EC2 instance (no public IP) won´t have access internet via NAT but VPC endpoints, some extra works are required
- 4.1 Create VPC endpoints for System Manager. Remember to allow HTTPS (port 443) outbound traffic in security group for your endpoint (ssm, ssmmessages and ec2messages)
- 4.2. Create an IAM Role as EC2 profile that contains at least the following 2 policies
- aws managed policy AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore
- a custom policy for accessing an AWS owned S3 buckets.
- 4.3 Attach this instance profile to your EC2 instance
- 4.4 Make sure enable “DNS resolution” and “DNS hostnames” for you VPC
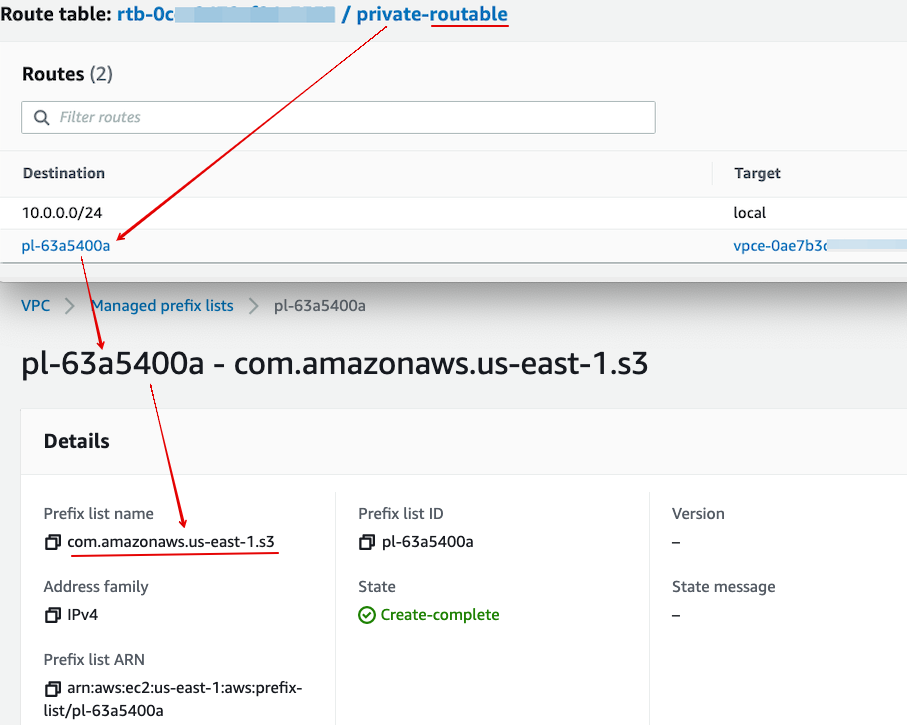
- 4.5 In addition, if your EC2 instance need to access other AWS services such as S3, remember to create needed endpoints for them as well. (For S3 you can choose either Gateway or Endpoint. At this moment Gateway is free.) Note that you need to add the endpoint into the private subnet route table. The following screenshot shows the route table entity of a S3 Gateway endpoint, which is using prefix lists.
5. Verification
Once the SSM is fully up-and-running, the EC2 instance (either in public/private subnet) will appear in Fleet Manager in SSM web console.