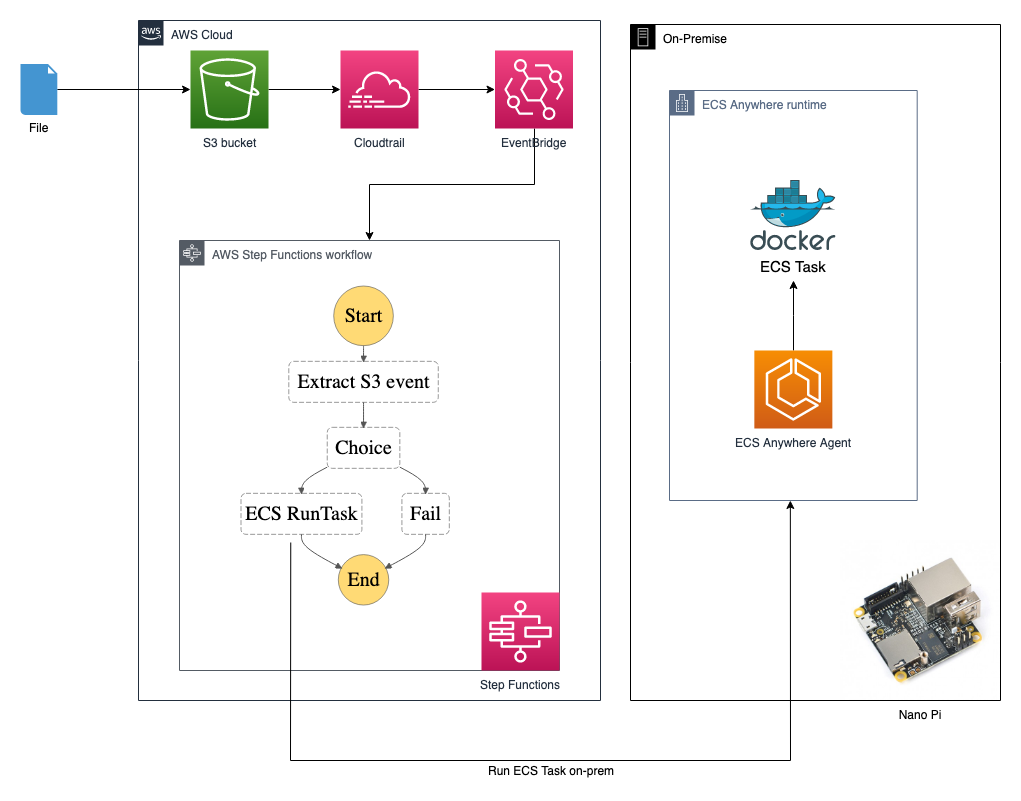
This is a demo solution that is using AWS Step Functions and ECS Anywhere to complete a simple data processing task by using cloud orchestration (Step Functions) and local computing resources (a NanoPi).
Data flow
- User upload a file to a s3 bucket
- S3 triggers step functions via cloudtrail and event bridge
- Event bridge triggers a step function state machine
- State machine triggers a ECS Anywhere task to download the file from s3 to local (to do some processing), if file name matches condition
Architecture
NanoPi that runs ECS Anywhere

NanoPi Neo2 with LED hat in my home office, running AWS ECS Anywhere.
Source code
All source code can be found at https://github.com/linkcd/step-function-with-ecs-Anywhere-example
1. Build a docker image as the ECS Anywhere task
As in this demo, the ecs Anywhere is running on a Nanopi, it should be build on the Pi as it is ARM architecture
1 | # In nano pi ssh |
Then push to public repository so ECS cluster can download (public docker hub or private ECR)
2. Setup ECS Anywhere and tasks
- Setup ECS Anywhere cluster on Nanopi
- Create an ECS execution role that has permission to download file from s3
- Create an ECS task (see ecs-task-definition.json) that refers to linkcd/s3downloader:arm image
3. Create a step function state machine
- Create a state machine (see state-machine-definition.json)
- As we need to wait for ecs task finish, step function requires permission as in here
- Follow the steps for setting up s3 triggers step functions via cloudtrail and event bridge
3.1 ECS task details:
(1). Start:
The s3 upload event is captured by cloudtrail, which triggers and pass the event data to step function.
(2). Extract S3 event
This PASS step extract the needed info (bucket name and file key). Output is
1 | { |
(3). Choice
The CHOICE step check the file key and trigger the ECS task ONLY IF the file key matches “demo*.txt”
(4). ECS RunTask
This ECS RunTask update the input paramater (adding s3:// prefix to bucket name), then pass the parameters to ecs Anywhere task via environment variables.
(5). End
Once the ecs Anywhere task is finished, the downloaded file can be found in the ecs Anywhere local file system (in this case, the file is in /data)
4. Side notes
In ECS RunTask in Step Functions, override command cannot pass multiple parameters. In our case we would like to use aws cli docker for simple aws cli s3 download. However if we override the command to “s3 cp x y” in ECS RunTask step in State Machine, these 4 parts will NOT be passed as individual 4 parameters but ONE parameter that contains all. AWS cli cannot accept that.
Incorrect value that passed via override command
1 | "Args": [ |
Correct call if we directly use aws cli docker from terminal
1 | "Args": [ |
Therefore we use environment variables to make sure we can pass parameters to ecs container task separately (it means we have to use our own container)